由于以前也做过很多兑换码的功能,但是也没有考虑过大量的兑换码的情况,所以这里尝试实现了一个生成与兑换的方案,分享出来。当然这不一定是最好的解决方案,这里仅供大家参考。有什么问题或可以优化的地方欢迎留言讨论。
*此方案可以根据输入的兑换码数量以及兑换码的字符长度来生成兑换码,每次生成兑换码的最大数量为int的最大值,一般为2147483647,即21亿个。
*此方案不需要数据库存储已生成的兑换码,直接使用验证算法即可验证兑换码是否有效。
*注意此算法的最短兑换码长度为12。这里可以根据需求对兑换码的结构进行调整来减少此长度。
首先说下思路
每一位兑换码有4部分构成:
[类型(1),id(4),随机码(n),校验码(1)]
类型为每次生成兑换码的组id,这里只用了1个byte来存储,可以根据需要增加。
id为每次生成的每个兑换码的唯一id。
随机码为每个兑换码的随机数。
校验码用来在验证兑换码时进行校验。
生成过程:
1.根据输入的兑换码总长度计算出随机码的位数,然后对每一位随机赋值。
2.把类型,id和随机码组成一个byte数组,计算总和,然后对byte.max进行取余运算,结果最为校验码。把校验码放在数组最末尾。
3.因为前面的时间和id有一定的规律性,我们使用随机码对时间和id进行异或操作,使兑换码看起来没有规律。
4.为了更加安全,我们使用一个密码对全部数据按顺序进行异或运算,这样即使知道了算法,在不知道密码的情况些也很难对数据进行破解。
5.我们使用32位的编码表来表示二进制数据,但是每个byte位长度为8,能表示127个数据,所以这里我们要对原数据进行拆分,32位编码表只需要5位就能表示,所以这里我们把原byte数组拆分为每5位为一个byte。如图:
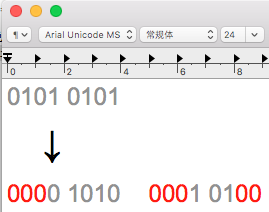
红色部分直接补0,末尾不足的部分也补充为0.这样一位数据就可以正好对应编码表中的一个数据。
6.把我们重新整理好的byte数组按照编码表转换位字符串就是我们最终的兑换码。
验证的过程就是把生成的过程反过来执行一遍。
下面给出完整代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 |
public class Redeem { static String stringtable = "abcdefghijkmnpqrstuvwxyz23456789"; final static String password = "dak3le2"; //从byte转为字符表索引所需要的位数 final static int convertByteCount = 5; public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception { ShowTime(); System.out.println("======================="); create((byte)1,10000,12,password); VerifyCode("c8dksqjamaba"); VerifyCode("4a36g5npamna"); VerifyCode("4a36g5naamna"); VerifyCode("dafe33234g435"); VerifyCode("ga8ehxsq6dja"); } /** * 生成兑换码 * 这里每一次生成兑换码的最大数量为int的最大值即2147483647 * @param time * @param id * @param count * @return */ public static byte[] create(byte groupid,int codecount,int codelength,String password) { //8位的数据总长度 int fullcodelength = codelength * convertByteCount / 8; //随机码对时间和id同时做异或处理 //类型1,id4,随机码n,校验码1 int randcount = fullcodelength - 6;//随机码有多少个 //如果随机码小于0 不生成 if(randcount <= 0 ) { return null; } for(int i = 0 ; i < codecount ; i ++) { //这里使用i作为code的id //生成n位随机码 byte[] randbytes = new byte[randcount]; for(int j = 0 ; j < randcount ; j ++) { randbytes[j] = (byte)(Math.random() * Byte.MAX_VALUE); } //存储所有数据 ByteHapper byteHapper = ByteHapper.CreateBytes(fullcodelength); byteHapper.AppendNumber(groupid).AppendNumber(i).AppendBytes(randbytes); //计算校验码 这里使用所有数据相加的总和与byte.max 取余 byte verify = (byte) (byteHapper.GetSum() % Byte.MAX_VALUE); byteHapper.AppendNumber(verify); //使用随机码与时间和ID进行异或 for(int j = 0 ; j < 5 ; j ++) { byteHapper.bytes[j] = (byte) (byteHapper.bytes[j] ^ (byteHapper.bytes[5 + j % randcount])); } //使用密码与所有数据进行异或来加密数据 byte[] passwordbytes = password.getBytes(); for(int j = 0 ; j < byteHapper.bytes.length ; j++){ byteHapper.bytes[j] = (byte) (byteHapper.bytes[j] ^ passwordbytes[j % passwordbytes.length]); } //这里存储最终的数据 byte[] bytes = new byte[codelength]; //按6位一组复制给最终数组 for(int j = 0 ; j < byteHapper.bytes.length ; j ++) { for(int k = 0 ; k < 8 ; k ++) { int sourceindex = j*8+k; int targetindex_x = sourceindex / convertByteCount; int targetindex_y = sourceindex % convertByteCount; byte placeval = (byte)Math.pow(2, k); byte val = (byte)((byteHapper.bytes[j] & placeval) == placeval ? 1:0); //复制每一个bit bytes[targetindex_x] = (byte)(bytes[targetindex_x] | (val << targetindex_y)); } } StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); //编辑最终数组生成字符串 for(int j = 0 ; j < bytes.length ; j ++) { result.append(stringtable.charAt(bytes[j])); } System.out.println("out string : " + result.toString()); } ShowTime(); return null; } /** * 验证兑换码 * @param code */ public static void VerifyCode(String code ){ byte[] bytes = new byte[code.length()]; //首先遍历字符串从字符表中获取相应的二进制数据 for(int i=0;i<code.length();i++){ byte index = (byte) stringtable.indexOf(code.charAt(i)); bytes[i] = index; } //还原数组 int fullcodelength = code.length() * convertByteCount / 8; int randcount = fullcodelength - 6;//随机码有多少个 byte[] fullbytes = new byte[fullcodelength]; for(int j = 0 ; j < fullbytes.length ; j ++) { for(int k = 0 ; k < 8 ; k ++) { int sourceindex = j*8+k; int targetindex_x = sourceindex / convertByteCount; int targetindex_y = sourceindex % convertByteCount; byte placeval = (byte)Math.pow(2, targetindex_y); byte val = (byte)((bytes[targetindex_x] & placeval) == placeval ? 1:0); fullbytes[j] = (byte) (fullbytes[j] | (val << k)); } } //解密,使用密码与所有数据进行异或来加密数据 byte[] passwordbytes = password.getBytes(); for(int j = 0 ; j < fullbytes.length ; j++){ fullbytes[j] = (byte) (fullbytes[j] ^ passwordbytes[j % passwordbytes.length]); } //使用随机码与时间和ID进行异或 for(int j = 0 ; j < 5 ; j ++) { fullbytes[j] = (byte) (fullbytes[j] ^ (fullbytes[5 + j % randcount])); } //获取校验码 计算除校验码位以外所有位的总和 int sum = 0; for(int i = 0 ;i < fullbytes.length - 1; i ++){ sum += fullbytes[i]; } byte verify = (byte) (sum % Byte.MAX_VALUE); //校验 if(verify == fullbytes[fullbytes.length - 1]){ System.out.println(code + " : verify success!"); }else { System.out.println(code + " : verify failed!"); } } public static void ShowTime(){ Date date = new Date(); long times = date.getTime();//时间戳 System.out.println("time : " + times); } } |
这里为了方便还写了一个byte[]的辅助类:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 |
public class ByteHapper { //原始数组 byte[] bytes; //记录当前写入到多少位 int index; private ByteHapper(int capacity){ bytes = new byte[capacity]; index = 0; } public static ByteHapper CreateBytes(int capacity){ ByteHapper byteHapper = new ByteHapper(capacity); return byteHapper; } //向数组中追加内容 public ByteHapper AppendNumber(long val){ byte[] arr = Number2byte(val); AppendBytes(arr); return this; } public ByteHapper AppendNumber(int val){ byte[] arr = Number2byte(val); AppendBytes(arr); return this; } public ByteHapper AppendNumber(short val){ byte[] arr = Number2byte(val); AppendBytes(arr); return this; } public ByteHapper AppendNumber(byte val){ byte[] arr = new byte[]{val}; AppendBytes(arr); return this; } /** * 获取数据的总和 * @return */ public int GetSum(){ int ret = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < bytes.length ; i ++){ ret += bytes[i]; } return ret; } //追加byte数组 public ByteHapper AppendBytes(byte[] arr){ for(byte i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++){ bytes[index + i] = arr[i]; } index += arr.length; return this; } /** * 将数字转换为byte数组 */ public static byte[] Number2byte(long val) { byte[] arr = new byte[]{ (byte) ((val >> 56) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 48) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 40) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 32) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 24) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 16) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 8) & 0xFF), (byte) (val & 0xFF) }; return arr; } public static byte[] Number2byte(int val) { byte[] arr = new byte[]{ (byte) ((val >> 24) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 16) & 0xFF), (byte) ((val >> 8) & 0xFF), (byte) (val & 0xFF) }; return arr; } public static byte[] Number2byte(short val) { byte[] arr = new byte[]{ (byte) ((val >> 8) & 0xFF), (byte) (val & 0xFF) }; return arr; } } |
运行Redeem类可以看到如下输出:
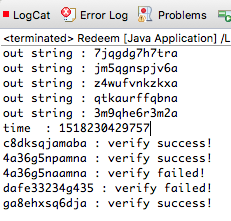
可以看到正确的码都可以验证成功,我们对原来的码做稍微的修改和随便输入的乱码都会验证失败。
这里在生成兑换码时,最后一步对原byte数组进行拆分操作,是生成一个新数组,然后根据原数组计算新数组中每一位的值,这里如果是在c/c++中会方便很多,直接只用指针访问地址,然后每5位操作一下就可以,但是在java暂时只能想到这种笨方法,不知道有没有更方便的方法,如果有,还请多多指教~~